
- #GIT LIST BRANCHES COMMAND FULL#
- #GIT LIST BRANCHES COMMAND SOFTWARE#
- #GIT LIST BRANCHES COMMAND CODE#
Git pull fetches the last uploaded changes from the remote server into the local repository so that you can have the latest updates from your teammates. If your branch is a newly created one, then you need to push the branch using the following command: git push -set-upstream or git push -u origin It will also create a named branch in the remote repository if it does not exist. The git push command pushes the committed file changes from the local repository to the remote repository so others can use them. Modify the last commit with the latest changes as a new commit: $ git commit -amend -m “" You can replace the two previous commands with the following single command: $ git commit -am “” Note: After running the above command, the default editor will open to provide a commit message.Ĭommit files with a message: $ git commit -m “” UsageĬommit any files added with the git add command and files that have been changed since then: $ git commit -a This commit message helps others understand the changes that have been done.
#GIT LIST BRANCHES COMMAND CODE#
Every time you commit your code changes, you have to include a brief description of the changes made. Git commit saves the changes in your local repository. UsageĪdd all new, modified, and deleted files: $ git add -AĪdd modified and deleted files: $ git add -u The git adds command adds your changes in a file to the staging area where you can compare your local version and the version on the remote repository.īefore you commit your new or modified file, it should be added to the staging area by using the git add command. Switch to an existing branch: git checkout Ĭreate and switch to a new branch: git checkout -b You can also use this command for checking out the files.
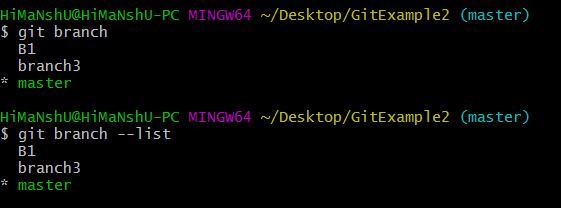
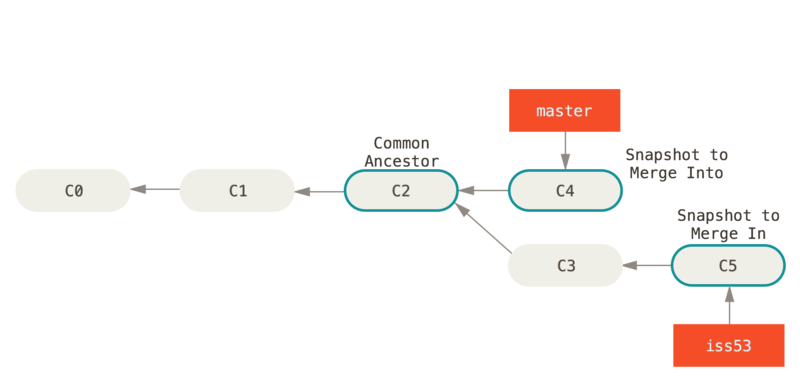
To achieve this, the branch you want to switch to should be present in your local system and the changes in your current branch should be committed or stashed before you make the switch. The git checkout command allows us to switch to an existing branch or create and switch to a new branch. View all branches and see which branch you’re currently working on: $ git branch or $ git branch -list List all the local and remote branches: $ git branch -a UsageĬreate a new branch locally: $ git branch Git branch lets us add a new branch to an existing branch, view all existing branches, and delete a branch. This command will add the original location as a remote location so you can pull changes from it and push changes to it if you have permission. When you clone a repository, the code will be automatically downloaded to your machine. Git clone creates a local working copy of the source code from a remote repository. You can also provide a repository name with the git init command. Go to the directory that contains your project files and run the git init command. This is the first command to start a new project in a GitHub repository. The git init command lets us create a new Git repository. In this article, you will learn the most helpful Git commands that will take you to the next level in development:

There are hundreds of Git commands, but only a few significant commands are used regularly.
#GIT LIST BRANCHES COMMAND FULL#
Nowadays, Git has become a must-have tool for any developer, and knowing Git commands is essential for developers to use Git to its full potential. With it, you can know who did what, when, and why. It helps developers easily handle different versions of a source code.
#GIT LIST BRANCHES COMMAND SOFTWARE#
Git is open-source software and distributed version control system. BoldSign – Electronic Signature Software.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
